Ratickle
Founding Member / Super Moderator
The Weather Channel noted the jump is the equivalent of adding 219,000 square miles to the worst drought categories -- "an area slightly larger than the states of California and New York combined," it noted.
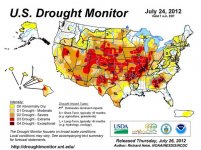
States posting dramatic increases in just the last week included Illinois, which went from 8 percent in extreme/exceptional drought to 70 percent, and Nebraska, which went from 5 percent to 64 percent.
"Over 90 percent of the topsoil was short or very short of moisture in Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, Missouri, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio, with virtually all (99 percent) short or very short in Missouri and Illinois," the monitor stated. "Over 80 percent of the pasture and rangeland was in poor or very poor condition in Kansas, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana."
A longer drought index compiled by the U.S. shows this year's drought now covers the most acreage since a dry spell in 1954. Two Dust Bowl years, 1934 and 1939, also had larger drought areas in the Palmer Drought Severity Index, which dates back to 1895 but is not as detailed as the Drought Monitor.
States posting dramatic increases in just the last week included Illinois, which went from 8 percent in extreme/exceptional drought to 70 percent, and Nebraska, which went from 5 percent to 64 percent.
"Over 90 percent of the topsoil was short or very short of moisture in Oklahoma, Kansas, Nebraska, Missouri, Iowa, Illinois, Indiana, and Ohio, with virtually all (99 percent) short or very short in Missouri and Illinois," the monitor stated. "Over 80 percent of the pasture and rangeland was in poor or very poor condition in Kansas, Arkansas, Missouri, Illinois, and Indiana."
A longer drought index compiled by the U.S. shows this year's drought now covers the most acreage since a dry spell in 1954. Two Dust Bowl years, 1934 and 1939, also had larger drought areas in the Palmer Drought Severity Index, which dates back to 1895 but is not as detailed as the Drought Monitor.

